
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Complications
- Influence of Glucose Fluctuation on Peripheral Nerve Damage in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Yu Ji Kim, Na Young Lee, Kyung Ae Lee, Tae Sun Park, Heung Yong Jin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):117-128. Published online September 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0275

- 5,221 View
- 179 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
It is unclear whether glycemic variability (GV) is a risk factor for diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), and whether control of GV is beneficial for DPN. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of GV on peripheral nerve damage by inducing glucose fluctuation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
Methods
Rats were divided into four groups: normal (normal glucose group [NOR]), diabetes without treatment (sustained severe hyperglycemia group; diabetes mellitus [DM]), diabetes+once daily insulin glargine (stable hyperglycemia group; DM+LAN), and diabetes+once daily insulin glargine with twice daily insulin glulisine (unstable glucose fluctuation group; DM+Lantus [LAN]+Apidra [API]). We measured anti-oxidant enzyme levels and behavioral responses against tactile, thermal, and pressure stimuli in the plasma of rats. We also performed a quantitative comparison of cutaneous and sciatic nerves according to glucose fluctuation.
Results
At week 24, intraepidermal nerve fiber density was less reduced in the insulin-administered groups compared to the DM group (P<0.05); however, a significant difference was not observed between the DM+LAN and DM+LAN+API groups irrespective of glucose fluctuation (P>0.05; 16.2±1.6, 12.4±2.0, 14.3±0.9, and 13.9±0.6 for NOR, DM, DM+LAN, and DM+LAN+API, respectively). The DM group exhibited significantly decreased glutathione levels compared to the insulin-administered groups (2.64±0.10 μmol/mL, DM+LAN; 1.93±0.0 μmol/mL, DM+LAN+API vs. 1.25±0.04 μmol/mL, DM; P<0.05).
Conclusion
Our study suggests that glucose control itself is more important than glucose fluctuation in the prevention of peripheral nerve damage, and intra-day glucose fluctuation has a limited effect on the progression of peripheral neuropathy in rats with diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glucose Fluctuation Inhibits Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Hippocampal Tissues and Exacerbates Cognitive Impairment in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
Haiyan Chi, Yujing Sun, Peng Lin, Junyu Zhou, Jinbiao Zhang, Yachao Yang, Yun Qiao, Deshan Liu, Eusebio Chiefari
Journal of Diabetes Research.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Artesunate Inhibits Apoptosis and Promotes Survival in Schwann Cells via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Axis in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Xin Zhang, Zhifang Liang, Ying Zhou, Fang Wang, Shan Wei, Bing Tan, Yujie Guo
Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin.2023; 46(6): 764. CrossRef - The Potential of Glucose Treatment to Reduce Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Apoptosis of Inflamed Neural Cells In Vitro
Juin-Hong Cherng, Shu-Jen Chang, Hsin-Da Tsai, Chung-Fang Chun, Gang-Yi Fan, Kenneth Dean Reeves, King Hei Stanley Lam, Yung-Tsan Wu
Biomedicines.2023; 11(7): 1837. CrossRef - Relationship between acute glucose variability and cognitive decline in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Haiyan Chi, Min Song, Jinbiao Zhang, Junyu Zhou, Deshan Liu, Victor Manuel Mendoza-Nuñez
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(9): e0289782. CrossRef
- Glucose Fluctuation Inhibits Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Hippocampal Tissues and Exacerbates Cognitive Impairment in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Status of Diabetic Neuropathy in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort Analysis (2006 to 2015) (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:115-9)
- Seong-Su Moon, Chong Hwa Kim, Seon Mee Kang, Eun Sook Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Jae-Seung Yun, Ho Chan Cho, Dae Jung Kim, Tae Sun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):459-460. Published online May 25, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0084
- 3,816 View
- 77 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
- Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:842-53)
- Sun Hee Kim, Tae Sun Park, Heung Yong Jin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):127-128. Published online January 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0289
- 3,372 View
- 98 Download
- Complications
- Status of Diabetic Neuropathy in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort Analysis (2006 to 2015)
- Seong-Su Moon, Chong Hwa Kim, Seon Mee Kang, Eun Sook Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Jae-Seung Yun, Ho Chan Cho, Dae Jung Kim, Tae Sun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):115-119. Published online December 18, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0120

- 7,042 View
- 275 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - This report presents the status of diabetic neuropathy (DN) in Korea as determined using a National Health Insurance ServiceNational Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC). Annual prevalences of DN were estimated by age and gender using descriptive statistics. Pharmacological treatments for DN were also analyzed. The annual prevalence of DN increased from 24.9% in 2006 to 26.6% in 2007, and thereafter, gradually subsided to 20.8% in 2015. In most cases, pharmacological treatments involved a single drug, which accounted for 91.6% of total prescriptions in 2015. The most commonly used drugs (in decreasing order) were thioctic acid, an anti-convulsive agent, or a tricyclic antidepressant. In conclusion, the prevalence of DN decreased over the 10-year study period. Thioctic acid monotherapy was usually prescribed for DN. To reduce the socio-economic burden of DN, more attention should be paid to the diagnosis of this condition and to the appropriate management of patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of cardiovascular events according to the tricyclic antidepressant dosage in patients with chronic pain: a retrospective cohort study
Hyunji Koo, Seung Hun You, Sewon Park, Kyeong Hye Jeong, Nakyung Jeon, Sun-Young Jung
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2023; 79(1): 159. CrossRef - How does diabetic peripheral neuropathy impact patients' burden of illness and the economy? A retrospective study in Beijing, China
Qi Pan, Sijia Fei, Lina Zhang, Huan Chen, Jingyi Luo, Weihao Wang, Fei Xiao, Lixin Guo
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Chronic disease management program applied to type 2 diabetes patients and prevention of diabetic complications: a retrospective cohort study using nationwide data
Min Kyung Hyun, Jang Won Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pharmacological and Nonpharmacological Treatments for Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Han Na Jang, Tae Jung Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 743. CrossRef - Are herbal medicines alone or in combination for diabetic peripheral neuropathy more effective than methylcobalamin alone? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Chang-Woo Lee, Joon-Soo Jin, Seungwon Kwon, Chul Jin, Seung-Yeon Cho, Seong-Uk Park, Woo-Sang Jung, Sang-Kwan Moon, Jung-Mi Park, Chang-Nam Ko, Ki-Ho Cho
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2022; 49: 101657. CrossRef - Pathogenesis and Treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Seon Mee Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(4): 222. CrossRef - Status of Diabetic Neuropathy in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort Analysis (2006 to 2015) (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:115-9)
Seong-Su Moon, Chong Hwa Kim, Seon Mee Kang, Eun Sook Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Jae-Seung Yun, Ho Chan Cho, Dae Jung Kim, Tae Sun Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 459. CrossRef - Status of Diabetic Neuropathy in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort Analysis (2006 to 2015) (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:115-9)
Tímea Csákvári, Diána Elmer, Lilla Horváth, Imre Boncz
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 454. CrossRef - Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)
Ja Young Jeon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 613. CrossRef - Diffculties and ways to overcome them in selection of therapy for pain syndromes in patients with diabetes mellitus
K. A. Makhinov, P. R. Kamchatnov
Medical alphabet.2021; (22): 25. CrossRef
- Risk of cardiovascular events according to the tricyclic antidepressant dosage in patients with chronic pain: a retrospective cohort study
- Drug/Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Treatment with Quadruple Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Multi-Center, Retrospective, Observational Study
- Jun Sung Moon, Sunghwan Suh, Sang Soo Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Jeong Mi Kim, Min Hee Jang, Kyung Ae Lee, Ju Hyung Lee, Seung Min Chung, Young Sang Lyu, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jung Eun Jang, Tae Nyun Kim, Sung Woo Kim, Eonju Jeon, Nan Hee Cho, Mi-Kyung Kim, Hye Soon Kim, Il Seong Nam-Goong, Eun Sook Kim, Jin Ook Chung, Dong-Hyeok Cho, Chang Won Lee, Young Il Kim, Dong Jin Chung, Kyu Chang Won, In Joo Kim, Tae Sun Park, Duk Kyu Kim, Hosang Shon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):675-683. Published online August 12, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0107
- 35,360 View
- 367 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
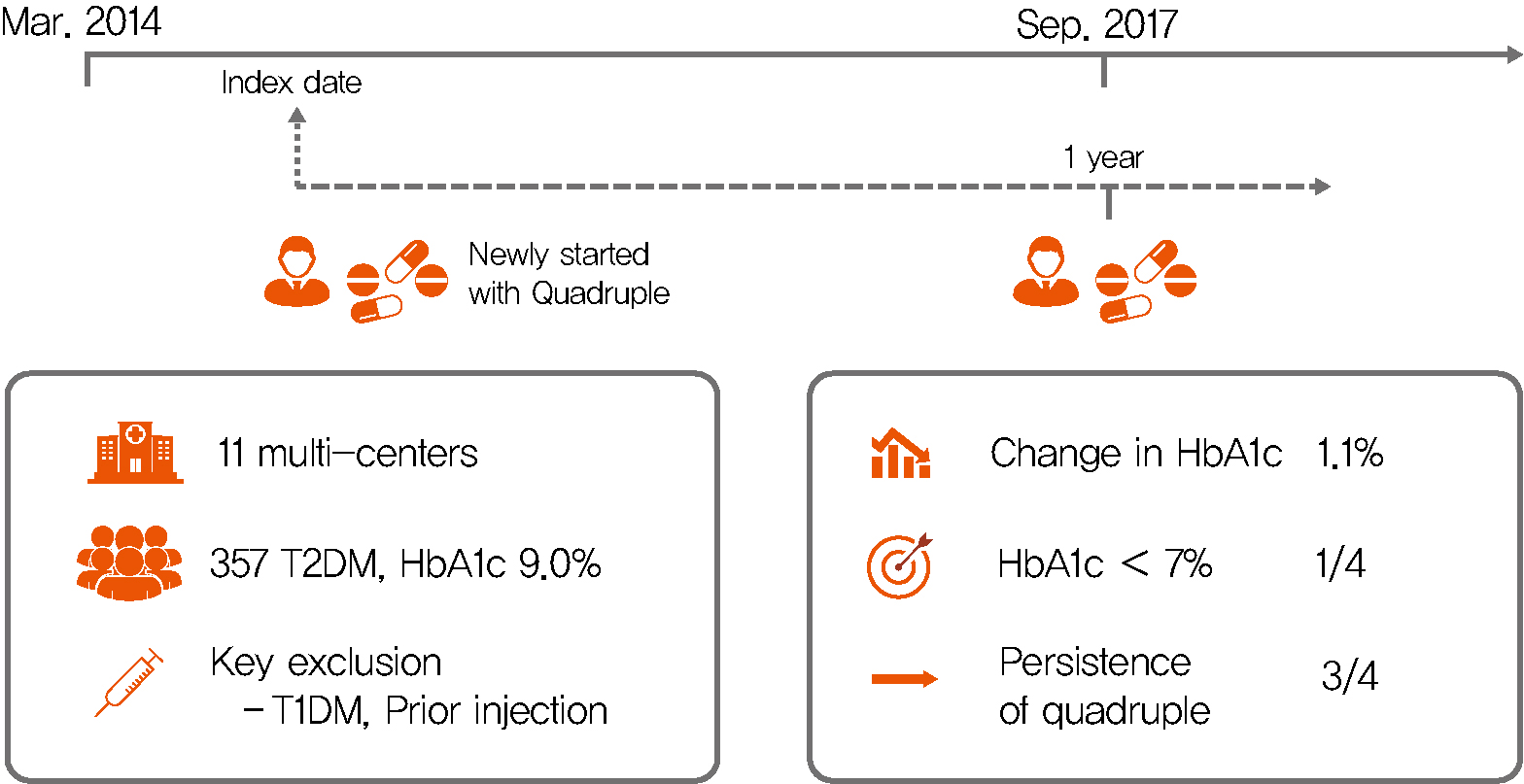
Background Only few studies have shown the efficacy and safety of glucose-control strategies using the quadruple drug combination. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to investigate the usefulness of the quadruple combination therapy with oral hypoglycemic agents (OHAs) in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods From March 2014 to December 2018, data of patients with T2DM, who were treated with quadruple hypoglycemic medications for over 12 months in 11 hospitals in South Korea, were reviewed retrospectively. We compared glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels before and 12 months after quadruple treatment with OHAs. The safety, maintenance rate, and therapeutic patterns after failure of the quadruple therapy were also evaluated.
Results In total, 357 patients were enrolled for quadruple OHA therapy, and the baseline HbA1c level was 9.0%±1.3% (74.9±14.1 mmol/mol). After 12 months, 270 patients (75.6%) adhered to the quadruple therapy and HbA1c was significantly reduced from 8.9%±1.2% to 7.8%±1.3% (mean change, −1.1%±1.2%;
P <0.001). The number of patients with HbA1c <7% increased significantly from 5 to 68 (P <0.005). In addition, lipid profiles and liver enzyme levels were also improved whereas no changes in body weight. There was no significant safety issue in patients treated with quadruple OHA therapy.Conclusion This study shows the therapeutic efficacy of the quadruple OHA regimen T2DM and demonstrates that it can be an option for the management of T2DM patients who cannot use insulin or reject injectable therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Estimating Type 2 Diabetes Prevalence: A Model of Drug Consumption Data
Rita Oliveira, Matilde Monteiro-Soares, José Pedro Guerreiro, Rúben Pereira, António Teixeira-Rodrigues
Pharmacy.2024; 12(1): 18. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin added to metformin plus gemigliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind, randomized, comparator-active study: ENHANCE-D study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Kyung Ah Han, Tae Nyun Kim, Cheol-Young Park, Jung Hwan Park, Sang Yong Kim, Yong Hyun Kim, Kee Ho Song, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Sik Kim, Gwanpyo Koh, Jun Goo Kang, Mi Kyung Kim, Ji Min Han, Nan Hee Kim, Ji Oh Mok, Jae Hyuk Lee, Soo Lim, Sang S
Diabetes & Metabolism.2023; 49(4): 101440. CrossRef - Effectiveness and safety of teneligliptin added to patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by oral triple combination therapy: A multicentre, randomized, double‐blind, and placebo‐controlled study
Minyoung Lee, Woo‐je Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Byung‐Wan Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(6): 1105. CrossRef - A double‐blind, Randomized controlled trial on glucose‐lowering EFfects and safety of adding 0.25 or 0.5 mg lobeglitazone in type 2 diabetes patients with INadequate control on metformin and dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor therapy: REFIND study
Soree Ryang, Sang Soo Kim, Ji Cheol Bae, Ji Min Han, Su Kyoung Kwon, Young Il Kim, Il Seong Nam‐Goong, Eun Sook Kim, Mi‐kyung Kim, Chang Won Lee, Soyeon Yoo, Gwanpyo Koh, Min Jeong Kwon, Jeong Hyun Park, In Joo Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(9): 1800. CrossRef - Glycaemic control with add‐on thiazolidinedione or a sodium‐glucose co‐transporter‐2 inhibitor in patients with type 2 diabetes after the failure of an oral triple antidiabetic regimen: A 24‐week, randomized controlled trial
Jaehyun Bae, Ji Hye Huh, Minyoung Lee, Yong‐Ho Lee, Byung‐Wan Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(2): 609. CrossRef
- Estimating Type 2 Diabetes Prevalence: A Model of Drug Consumption Data
- Drug/Regimen
- Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats
- Sun Hee Kim, Tae Sun Park, Heung Yong Jin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):842-853. Published online May 28, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0190
- 6,156 View
- 177 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
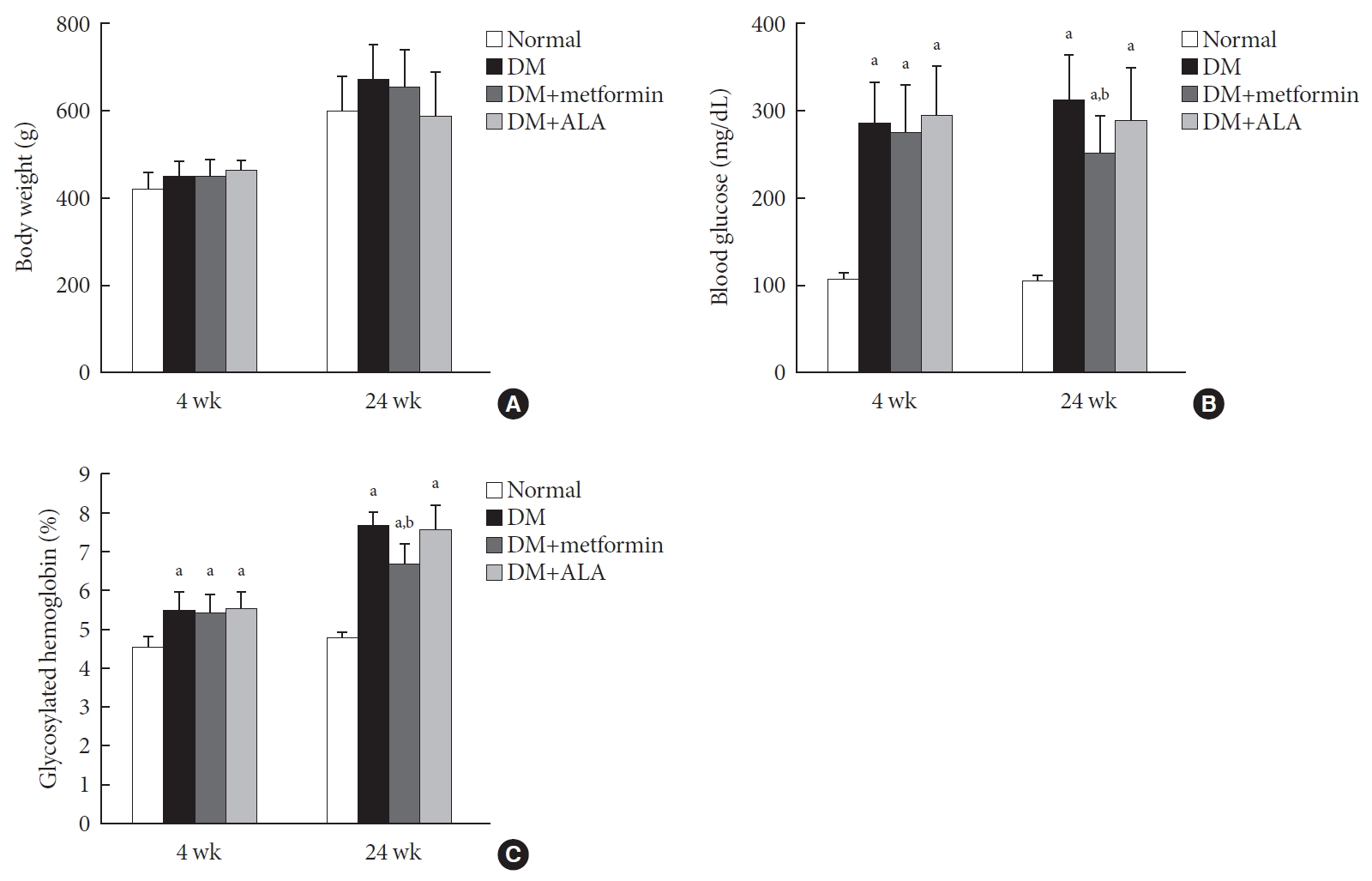
ePub Background Metformin is widely marketed medication for the treatment of diabetes, but its pharmacological effect on diabetic peripheral neuropathy remains unclear. In this study, the effect of metformin on peripheral nerves in diabetic rats was investigated using diverse neuronal parameters of nerve fibers.
Methods Rats were assigned to one of four groups (
n =7 to 10 per group): normal, diabetes mellitus (DM), DM+metformin (100 mg/kg), and DM+alpha lipoic acid (ALA, 100 mg/kg). DM was induced by streptozotocin/high-fat diet (STZ/HFD). After 12 weeks, the sensory thresholds to mechanical and heat stimuli were assessed. Repeated sensory tests, immunofluorescence microscopic comparison of peripheral nerves, and biochemical blood analysis were performed after 24 weeks.Results Both DM+metformin and DM+ALA groups showed similar trends to diverse sensory tests at 24 weeks compared to DM group although the degree of change were different according to the stimulated senses. There was no significant difference in the comparison of the intraepidermal nerve fiber density (IENFD) of peripheral nerves between the DM+metformin and DM+ALA groups (11.83±0.07 fibers/mm vs. 12.37±1.82 fibers/mm, respectively). Both groups showed preserved IENFD significantly compared with DM group (8.46±1.98 fibers/mm,
P <0.05). Sciatic nerve morphology of the experimental animals showed a similar trend to the IENFD, with respect to axonal diameter, myelin sheath thickness, and myelinated fiber diameter.Conclusion Metformin has beneficial pharmacological effects on the preservation of peripheral nerves in diabetic rats and its effects are comparable to those of ALA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metformin improves diabetic neuropathy by reducing inflammation through up-regulating the expression of miR-146a and suppressing oxidative stress
Fengmin Liu, Fangqin You, Lihang Yang, Siyun Wang, Diya Xie
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2024; 38(6): 108737. CrossRef - Effect of Metformin on the Functional and Electrophysiological Recovery of Crush Injury-Induced Facial Nerve Paralysis in Diabetic Rats
Kyung Hoon Sun, Cheol Hee Choi, Gwang-Won Cho, Chul Ho Jang
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(9): 1317. CrossRef - Is metformin neuroprotective against diabetes mellitus-induced neurodegeneration? An updated graphical review of molecular basis
Fatemeh Karami, Hamidreza Jamaati, Natalie Coleman-Fuller, Maryam Shokrian Zeini, A. Wallace Hayes, Mina Gholami, Mahsa Salehirad, Mohammad Darabi, Majid Motaghinejad
Pharmacological Reports.2023; 75(3): 511. CrossRef - Early Diagnosis through Estimation of Inflammatory Biomarkers and the Neuroprotective Role of Metformin in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Laxmi Sri, Prabhakar Orsu
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Nanotechnology(IJPSN).2023; 16(2): 6427. CrossRef - Bidirectional association between diabetic peripheral neuropathy and vitamin B12 deficiency: Two longitudinal 9-year follow-up studies using a national sample cohort
Heung Yong Jin, Kyung Ae Lee, Yu Ji Kim, In Sun Gwak, Tae Sun Park, Sang Woo Yeom, Jong Seung Kim
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(5): 436. CrossRef - An overview of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Diagnosis and treatment advancements
Jonathan M. Hagedorn, Alyson M. Engle, Tony K. George, Jay Karri, Newaj Abdullah, Erik Ovrom, Jhon E. Bocanegra-Becerra, Ryan S. D'Souza
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 188: 109928. CrossRef - The role of MicroRNA networks in tissue-specific direct and indirect effects of metformin and its application
Qinzhi Yang, Gang Wang, Dan Fang, Xiaojun Gao, Yu Liang, Liqun Wang, Jianbo Wu, Min Zeng, Mao Luo
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 151: 113130. CrossRef - Is metformin a possible treatment for diabetic neuropathy?
Juechun Wei, Yanling Wei, Meiyan Huang, Peng Wang, Shushan Jia
Journal of Diabetes.2022; 14(10): 658. CrossRef - Metformin as a potential therapeutic for neurological disease: mobilizing AMPK to repair the nervous system
Sarah Demaré, Asha Kothari, Nigel A. Calcutt, Paul Fernyhough
Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics.2021; 21(1): 45. CrossRef - Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:842-53)
Bo Kyung Koo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(1): 125. CrossRef - Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:842-53)
Sun Hee Kim, Tae Sun Park, Heung Yong Jin
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(1): 127. CrossRef - Impacts of statin and metformin on neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Korean Health Insurance data
Hong Ki Min, Se Hee Kim, Jong Han Choi, Kyomin Choi, Hae-Rim Kim, Sang-Heon Lee
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(33): 10198. CrossRef
- Metformin improves diabetic neuropathy by reducing inflammation through up-regulating the expression of miR-146a and suppressing oxidative stress
- Drug/Regimen
- γ-Linolenic Acid versus α-Lipoic Acid for Treating Painful Diabetic Neuropathy in Adults: A 12-Week, Double-Placebo, Randomized, Noninferiority Trial
- Jong Chul Won, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Seong-Su Moon, Sung Wan Chun, Chong Hwa Kim, Ie Byung Park, In Joo Kim, Jihyun Lee, Bong Yun Cha, Tae Sun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):542-554. Published online November 4, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0099
- 7,971 View
- 245 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background This study was a multicenter, parallel-group, double-blind, double-dummy, randomized, noninferiority trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of γ-linolenic acid (GLA) relative to α-lipoic acid (ALA) over a 12-week treatment period in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN).
Methods This study included 100 T2DM patients between 20 and 75 years of age who had painful DPN and received either GLA (320 mg/day) and placebo or ALA (600 mg/day) and placebo for 12 weeks. The primary outcome measures were mean changes in pain intensities as measured by the visual analogue scale (VAS) and the total symptom scores (TSS).
Results Of the 100 subjects who initially participated in the study, 73 completed the 12-week treatment period. Per-protocol analyses revealed significant decreases in the mean VAS and TSS scores compared to baseline in both groups, but there were no significant differences between the groups. The treatment difference for the VAS (95% confidence interval [CI]) between the two groups was −0.65 (−1.526 to 0.213) and the upper bound of the 95% CI did not exceed the predefined noninferiority margin (δ1=0.51). For the TSS, the treatment difference was −0.05 (−1.211 to 1.101) but the upper bound of the 95% CI crossed the noninferiority margin (δ2=0.054). There were no serious adverse events associated with the treatments.
Conclusion GLA treatment in patients with painful DPN was noninferior to ALA in terms of reducing pain intensity measured by the VAS over 12 weeks.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cell metabolism pathways involved in the pathophysiological changes of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Yaowei Lv, Xiangyun Yao, Xiao Li, Yuanming Ouyang, Cunyi Fan, Yun Qian
Neural Regeneration Research.2024; 19(3): 598. CrossRef - Diyabet Tedavisinde Antioksidan Etki: Alfa Lipoik Asit
Umut DALMIŞ, Emine Merve EKİCİ
Avrasya Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2024; 7(1): 68. CrossRef - Ranking Alpha Lipoic Acid and Gamma Linolenic Acid in Terms of Efficacy and Safety in the Management of Adults With Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis
Mario B. Prado, Karen Joy B. Adiao
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive comparison of a new technology with traditional methods for extracting Ougan (Citrus reticulata cv. Suavissima) seed oils: Physicochemical properties, fatty acids, functional components, and antioxidant activities
Huaxia Yang, Yudan Lin, Xiaoxu Zhu, Haishuo Mu, Yi Li, Shuangyang Chen, Jia Li, Xuedan Cao
LWT.2024; 197: 115857. CrossRef - Genetic and Transcriptomic Background of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidative Therapies in Late Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review
Gašper Tonin, Vita Dolžan, Jasna Klen
Antioxidants.2024; 13(3): 277. CrossRef - Alpha-lipoic acid activates AMPK to protect against oxidative stress and apoptosis in rats with diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Tianya Zhang, Dong Zhang, Zhihong Zhang, Jiaxin Tian, Jingwen An, Wang Zhang, Ying Ben
Hormones.2023; 22(1): 95. CrossRef - Pathogenetic treatments for diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Dan Ziegler
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 206: 110764. CrossRef - Omega-3 Nutrition Therapy for the Treatment of Diabetic Sensorimotor
Polyneuropathy
Deepak Menon, Evan J. H. Lewis, Bruce A. Perkins, Vera Bril
Current Diabetes Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Alpha-Lipoic Acid in the Treatment of Diabetic Neuropathy: A Systematic Review
Saleh A Abubaker, Abdulaziz M Alonazy, Albasseet Abdulrahman
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Insight into the possible mechanism(s) involved in the antinociceptive and antineuropathic activity of Descurainia sophia L. Webb ex Prantl essential oil
Donya Ziafatdoost Abed, Sajjad Jabbari, Zainul Amiruddin Zakaria, Saeed Mohammadi
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2022; 298: 115638. CrossRef - A novel approach to alpha-lipoic acid therapy in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Alicja Sementina, Mateusz Cierzniakowski, Julia Rogalska, Izabela Piechowiak, Marek Spichalski, Aleksandra Araszkiewicz
Journal of Medical Science.2022; : e714. CrossRef - Pathogenesis and Treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Seon Mee Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(4): 222. CrossRef - Diabetic Neuropathy: a Critical, Narrative Review of Published Data from 2019
Ameet S. Nagpal, Jennifer Leet, Kaitlyn Egan, Rudy Garza
Current Pain and Headache Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Therapeutic Potential of Ursolic Acid in Cancer and Diabetic Neuropathy Diseases
Manzar Alam, Sabeeha Ali, Sarfraz Ahmed, Abdelbaset Mohamed Elasbali, Mohd Adnan, Asimul Islam, Md. Imtaiyaz Hassan, Dharmendra Kumar Yadav
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(22): 12162. CrossRef - Diagnosis and treatment of the early stages of diabetic polyneuropathy
V. N. Khramilin, A. N. Zavyalov, I. Yu. Demidova
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2020; (7): 56. CrossRef
- Cell metabolism pathways involved in the pathophysiological changes of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Effectiveness and Safety of Adding Basal Insulin Glargine in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Exhibiting Inadequate Response to Metformin and DPP-4 Inhibitors with or without Sulfonylurea
- Yu Mi Kang, Chang Hee Jung, Seung-Hwan Lee, Sang-Wook Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Sin Gon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim, Young Min Cho, Tae Sun Park, Bon Jeong Ku, Gwanpyo Koh, Dol Mi Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Joong-Yeol Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(4):432-446. Published online June 19, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0092
- 5,558 View
- 90 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background We aimed to investigate the effectiveness and safety of adding basal insulin to initiating dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor and metformin and/or sulfonylurea (SU) in achieving the target glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods This was a single-arm, multicenter, 24-week, open-label, phase 4 study in patients with inadequately controlled (HbA1c ≥7.5%) T2DM despite the use of DPP-4 inhibitor and metformin. A total of 108 patients received insulin glargine while continuing oral antidiabetic drugs (OADs). The primary efficacy endpoint was the percentage of subjects achieving HbA1c ≤7.0%. Other glycemic profiles were also evaluated, and the safety endpoints were adverse events (AEs) and hypoglycemia.
Results The median HbA1c at baseline (8.9%; range, 7.5% to 11.1%) decreased to 7.6% (5.5% to 11.7%) at 24 weeks. Overall, 31.7% subjects (
n =33) achieved the target HbA1c level of ≤7.0%. The mean differences in body weight and fasting plasma glucose were 1.2±3.4 kg and 56.0±49.8 mg/dL, respectively. Hypoglycemia was reported in 36 subjects (33.3%, 112 episodes), all of which were fully recovered. There was no serious AE attributed to insulin glargine. Body weight change was significantly different between SU users and nonusers (1.5±2.5 kg vs. −0.9±6.0 kg,P =0.011).Conclusion The combination add-on therapy of insulin glargine, on metformin and DPP-4 inhibitors with or without SU was safe and efficient in reducing HbA1c levels and thus, is a preferable option in managing T2DM patients exhibiting dysglycemia despite the use of OADs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glycaemic control with add‐on thiazolidinedione or a sodium‐glucose co‐transporter‐2 inhibitor in patients with type 2 diabetes after the failure of an oral triple antidiabetic regimen: A 24‐week, randomized controlled trial
Jaehyun Bae, Ji Hye Huh, Minyoung Lee, Yong‐Ho Lee, Byung‐Wan Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(2): 609. CrossRef - Beneficial effect of anti-diabetic drugs for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung-Soo Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2020; 26(4): 430. CrossRef
- Glycaemic control with add‐on thiazolidinedione or a sodium‐glucose co‐transporter‐2 inhibitor in patients with type 2 diabetes after the failure of an oral triple antidiabetic regimen: A 24‐week, randomized controlled trial
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Tae Jung Oh, Jae Myung Yu, Kyung Wan Min, Hyun Shik Son, Moon Kyu Lee, Kun Ho Yoon, Young Duk Song, Joong Yeol Park, In Kyung Jeong, Bong Soo Cha, Yong Seong Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, In Joo Kim, Doo Man Kim, Sung Rae Kim, Kwan Woo Lee, Jeong Hyung Park, In Kyu Lee, Tae Sun Park, Sung Hee Choi, Sung Woo Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(3):276-286. Published online December 7, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0051
- 7,052 View
- 98 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Combination of metformin to reduce the fasting plasma glucose level and an α-glucosidase inhibitor to decrease the postprandial glucose level is expected to generate a complementary effect. We compared the efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose combination of voglibose plus metformin (vogmet) with metformin monotherapy in drug-naïve newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods A total of 187 eligible patients aged 20 to 70 years, with a glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level of 7.0% to 11.0%, were randomized into either vogmet or metformin treatments for 24 weeks. A change in the HbA1c level from baseline was measured at week 24.
Results The reduction in the levels of HbA1c was −1.62%±0.07% in the vogmet group and −1.31%±0.07% in the metformin group (
P =0.003), and significantly more vogmet-treated patients achieved the target HbA1c levels of <6.5% (P =0.002) or <7% (P =0.039). Glycemic variability was also significantly improved with vogmet treatment, estimated by M-values (P =0.004). Gastrointestinal adverse events and hypoglycemia (%) were numerically lower in the vogmet-treated group. Moreover, a significant weight loss was observed with vogmet treatment compared with metformin (−1.63 kg vs. −0.86 kg,P =0.039).Conclusion Vogmet is a safe antihyperglycemic agent that controls blood glucose level effectively, yields weight loss, and is superior to metformin in terms of various key glycemic parameters without increasing the risk of hypoglycemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Phytochemical analysis and antihyperglycemic activity of Castilleja arvensis
Mónica Aideé Díaz-Román, Juan José Acevedo-Fernández, Gabriela Ávila-Villarreal, Elizabeth Negrete-León, A. Berenice Aguilar-Guadarrama
Fitoterapia.2024; 174: 105839. CrossRef - YAP/TAZ axis was involved in the effects of metformin on breast cancer
Yu Xu, Hongke Cai, Yuanfeng Xiong, Li Tang, Longjiang Li, Li Zhang, Yi Shen, Yongqiang Yang, Ling Lin, Jiayi Huang
Journal of Chemotherapy.2023; 35(7): 627. CrossRef - Diabetes remission: Myth or reality?
Ashok Kumar, ShubhaLaxmi Margekar, Ravi Kumar
Indian Journal of Medical Specialities.2023; 14(1): 3. CrossRef - Analysis of Reports Sent to the Portuguese Pharmacovigilance System and Published Literature Regarding the Safety of Metformin in the Elderly
Beatriz Esteves, Cristina Monteiro, Ana Paula Coelho Duarte
Healthcare.2023; 11(15): 2197. CrossRef - Rapid prediction method of α-Glycosidase inhibitory activity of Coreopsis tinctoria extract from different habitats by near infrared spectroscopy
Xiaogang He, Xiang Han, Jiaping Yu, Yulong Feng, Ganghui Chu
Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy.2022; 268: 120601. CrossRef - Insulin autoimmune syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes: A report of two cases
Y. Shin, T.J. Oh, S.H. Choi, H.C. Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism.2021; 47(1): 101115. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Treatment with Quadruple Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Multi-Center, Retrospective, Observational Study
Jun Sung Moon, Sunghwan Suh, Sang Soo Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Jeong Mi Kim, Min Hee Jang, Kyung Ae Lee, Ju Hyung Lee, Seung Min Chung, Young Sang Lyu, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jung Eun Jang, Tae Nyun Kim, Sung Woo Kim, Eonju Jeon, Nan Hee Cho, Mi-Kyung Ki
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 675. CrossRef - Quantifying Remission Probability in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Sanjay Kalra, Ganapathi Bantwal, Nitin Kapoor, Rakesh Sahay, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Beatrice Anne, Raju A Gopal, Sunil Kota, Ashok Kumar, Ameya Joshi, Debmalya Sanyal, Mangesh Tiwaskar, Ashok Kumar Das
Clinics and Practice.2021; 11(4): 850. CrossRef - The effect of voglibose on metabolic profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials
Peyman Nowrouzi-Sohrabi, Reza Tabrizi, Shahla Rezaei, Fatemeh Jafari, Kamran Hessami, Mehdi Abedi, Mohammad Jalali, Pedram Keshavarzi, Saeed Shahabi, Ali Asghar Kolahi, Kristin Carson-Chahhoud, Amirhossein Sahebkar, Saeid Safiri
Pharmacological Research.2020; 159: 104988. CrossRef - Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Metabolism of Voglibose In Vitro and In Vivo
Mahesh Raj Nepal, Mi Jeong Kang, Geon Ho Kim, Dong Ho Cha, Ju-Hyun Kim, Tae Cheon Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 908. CrossRef - Response: Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (Diabetes metab J 2019;43;276-86)
Tae Jung Oh, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 547. CrossRef - Letter: Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43;276-86)
Hannah Seok, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 545. CrossRef
- Phytochemical analysis and antihyperglycemic activity of Castilleja arvensis
- Complications
- Effect of Empagliflozin, a Selective Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor, on Kidney and Peripheral Nerves in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Kyung Ae Lee, Heung Yong Jin, Na Young Lee, Yu Ji Kim, Tae Sun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(4):338-342. Published online April 25, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0095
- 3,991 View
- 64 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader The effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on peripheral nerves and kidneys in diabetes mellitus (DM) remains unexplored. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the effect of empagliflozin in diabetic rats. DM in rats was induced by streptozotocin injection, and diabetic rats were treated with empagliflozin 3 or 10 mg/kg. Following 24-week treatment, response thresholds to four different stimuli were tested and found to be lower in diabetic rats than in normal rats. Empagliflozin significantly prevented hypersensitivity (
P <0.05) and the loss of skin intraepidermal nerve fibers, and mesangial matrix expansion in diabetic rats. Results of this study demonstrate the potential therapeutic effects of empagliflozin for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy and nephropathy.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of empagliflozin in peripheral diabetic neuropathy of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Sahar Mohamed El-Haggar, Yasser Mostafa Hafez, Amira Mohamed El Sharkawy, Maha Khalifa
Medicina Clínica.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review of Recent Pharmacological Advances in the Management of Diabetes-Associated Peripheral Neuropathy
Osman Syed, Predrag Jancic, Nebojsa Nick Knezevic
Pharmaceuticals.2023; 16(6): 801. CrossRef - Renal intrinsic cells remodeling in diabetic kidney disease and the regulatory effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors
Wenwen Guo, Han Li, Yixuan Li, Wen Kong
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 165: 115025. CrossRef - A systematic review on renal effects of SGLT2 inhibitors in rodent models of diabetic nephropathy
Aqsa Ashfaq, Myriam Meineck, Andrea Pautz, Ebru Arioglu-Inan, Julia Weinmann-Menke, Martin C. Michel
Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2023; 249: 108503. CrossRef - The impact of canagliflozin on the risk of neuropathy events: A post-hoc exploratory analysis of the CREDENCE trial
Jinlan Liao, Amy Kang, Chao Xia, Tamara Young, Gian Luca Di Tanna, Clare Arnott, Carol Pollock, Arun V. Krishnan, Rajiv Agarwal, George Bakris, David M. Charytan, Dick de Zeeuw, Hiddo J.L. Heerspink, Adeera Levin, Bruce Neal, David C. Wheeler, Hong Zhang,
Diabetes & Metabolism.2022; 48(4): 101331. CrossRef - Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor Protects Against Diabetic Neuropathy and Nephropathy in Modestly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes: Follow-Up Study
Fukashi Ishibashi, Aiko Kosaka, Mitra Tavakoli
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Protective effect of empagliflozin on gentamicin-induced acute renal injury via regulation of SIRT1/NF-κB signaling pathway
Sandy R. Botros, Asmaa I. Matouk, Aliaa Anter, Mohamed M.A. Khalifa, Gehan H. Heeba
Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology.2022; 94: 103907. CrossRef - Empagliflozin mitigates type 2 diabetes-associated peripheral neuropathy: a glucose-independent effect through AMPK signaling
Noha F. Abdelkader, Marawan A. Elbaset, Passant E. Moustafa, Sherehan M. Ibrahim
Archives of Pharmacal Research.2022; 45(7): 475. CrossRef - Pathogenesis and Treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Seon Mee Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(4): 222. CrossRef - Empagliflozin and neohesperidin protect against methotrexate-induced renal toxicity via suppression of oxidative stress and inflammation in male rats
Adel T. Osman, Souty M.Z. Sharkawi, Mohamed I.A. Hassan, Amira M. Abo-youssef, Ramadan A.M. Hemeida
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2021; 155: 112406. CrossRef - Effect of exenatide on peripheral nerve excitability in type 2 diabetes
Tushar Issar, Natalie C.G. Kwai, Ann M. Poynten, Ria Arnold, Kerry-Lee Milner, Arun V. Krishnan
Clinical Neurophysiology.2021; 132(10): 2532. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Empagliflozin With Vitamin D Supplementation in Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Sanjana Mehta, Parminder Nain, Bimal K Agrawal, Rajinder P Singh, Jaspreet Kaur, Sabyasachi Maity, Aniruddha Bhattarcharjee, Jagannadha Peela, Shreya Nauhria, Samal Nauhria
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting oxidative stress, proinflammatory cytokines, apoptosis and toll like receptor 4 by empagliflozin to ameliorate bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis
Ahmed M. Kabel, Remon S. Estfanous, Majed M. Alrobaian
Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology.2020; 273: 103316. CrossRef - Empagliflozin reduces high glucose-induced oxidative stress and miR-21-dependent TRAF3IP2 induction and RECK suppression, and inhibits human renal proximal tubular epithelial cell migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Nitin A. Das, Andrea J. Carpenter, Anthony Belenchia, Annayya R. Aroor, Makoto Noda, Ulrich Siebenlist, Bysani Chandrasekar, Vincent G. DeMarco
Cellular Signalling.2020; 68: 109506. CrossRef - Differential Effects of Empagliflozin on Microvascular Complications in Murine Models of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Stephanie A. Eid, Phillipe D. O’Brien, Lucy M. Hinder, John M. Hayes, Faye E. Mendelson, Hongyu Zhang, Lixia Zeng, Katharina Kretzler, Samanthi Narayanan, Steven F. Abcouwer, Frank C. Brosius, Subramaniam Pennathur, Masha G. Savelieff, Eva L. Feldman
Biology.2020; 9(11): 347. CrossRef - Pre-treatment with Empagliflozin ameliorates Cisplatin induced acute kidney injury by suppressing apoptosis
Maaly A. Abd Elmaaboud, Ahmed M. Kabel, Mohamed Elrashidy
Journal of Applied Biomedicine.2019; 17(1): 90. CrossRef - Effects of ticagrelor, empagliflozin and tamoxifen against experimentally-induced vascular reactivity defects in rats in vivo and in vitro
Yasmin Moustafa Ahmed, Basim Anwar Shehata Messiha, Mahmoud El-Sayed El-Daly, Ali Ahmed Abo-Saif
Pharmacological Reports.2019; 71(6): 1034. CrossRef - SGLT2 inhibition with empagliflozin attenuates myocardial oxidative stress and fibrosis in diabetic mice heart
Chenguang Li, Jie Zhang, Mei Xue, Xiaoyu Li, Fei Han, Xiangyang Liu, Linxin Xu, Yunhong Lu, Ying Cheng, Ting Li, Xiaochen Yu, Bei Sun, Liming Chen
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Empagliflozin Contributes to Polyuria via Regulation of Sodium Transporters and Water Channels in Diabetic Rat Kidneys
Sungjin Chung, Soojeong Kim, Mina Son, Minyoung Kim, Eun Sil Koh, Seok Joon Shin, Seung-Hyun Ko, Ho-Shik Kim
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of empagliflozin in peripheral diabetic neuropathy of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Complication
- Morphologic Comparison of Peripheral Nerves in Adipocyte Tissue from
db/db Diabetic versus Normal Mice - Kyung Ae Lee, Na Young Lee, Tae Sun Park, Heung Yong Jin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(2):169-172. Published online March 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.42.2.169
- 3,397 View
- 43 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Present study investigated the morphologic changes of autonomic nerves in the adipose tissue in diabetic animal model. Male obese type 2 diabetic
db/db mice and age matched non-diabeticdb/m control mice were used. Epididymal adipose tissue from diabeticdb/db mice with that from control heterozygousdb/m mice was compared using confocal microscopy-based method to visualize intact whole adipose tissue. Immunohistochemistry with tyrosine hydroxylase for sympathetic (SP), choline acetyltransferase for parasympathetic (PSP), and protein gene product 9.5 (PGP 9.5) for whole autonomic nerves was performed. The quantity of immunostained portion of SP, PSP, and PGP 9.5 stained nerve fibers showed decreased trend in diabetic group; however, the ratio of SP/PSP of adipose tissue was higher in diabetic group compared with control group as follows (0.70±0.30 vs. 0.95±0.25,P <0.05; normal vs. diabetic, respectively). Both SP and PSP nerve fibers were observed in white adipose tissue and PSP nerve fibers were suggested as more decreased in diabetes based on our observation.
- Epidemiology
- Dietary Sodium Intake in People with Diabetes in Korea: The Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for 2008 to 2010
- Myung Shin Kang, Chong Hwa Kim, Su Jin Jeong, Tae Sun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(4):290-296. Published online June 23, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.4.290
- 3,420 View
- 40 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Diabetics are likely to receive advice from their physicians concerning lifestyle changes. To understand how much sodium is consumed by diabetics in Korea, we compared the average daily sodium intake between diabetics and non-diabetics after controlling for confounding factors.
Methods We obtained the sodium intake data for 13,957 individuals who participated in the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), 2008 to 2010, which consisted of a health interview and behavioral and nutritional surveys. The KNHANES uses a stratified, multistage, probability-sampling design, and weighting adjustments were conducted to represent the entire population.
Results Our analysis revealed that, overall, diabetics tended to have lower sodium intake (4,910.2 mg) than healthy individuals (5,188.2 mg). However, both diabetic and healthy individuals reported higher sodium intake than is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO). Stratified subgroup analyses revealed that the sodium intake (4,314.2 mg) among newly diagnosed diabetics was higher among women when compared to patients with known diabetes (3,812.5 mg,
P =0.035). Female diabetics with cardiovascular disease had lower average sodium intake compared to those without cardiovascular disease after adjusting for sex, age, body mass index, and total energy intake (P =0.058). Sodium intake among male diabetics with hypercholesterolemia (P =0.011) and female diabetics with hypertriglyceridemia (P =0.067) tended to be higher than that among those who without dyslipidemia.Conclusion The average sodium intake of diabetics in Korea was higher than the WHO recommends. Sodium intake in newly diagnosed diabetics was significantly higher than that in non-diabetics and previously diagnosed diabetics among females. Prospective studies are needed to identify the exact sodium intake.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Salt Intake in Adults with Diabetes and Hypertension: The Longitudinal Study of Adult Health-Brasil Study
Natália Gonçalves Ribeiro, Deborah F. Lelis, Rosane H. Griep, Sandhi M. Barreto, Maria del Carmen B Molina, Maria I. Schmidt, Bruce B. Duncan, Isabela Bensenor, Paulo A. Lotufo, José G. Mill, Marcelo Perim Baldo
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of different diets on glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes: A literature review
Maryam E Al-Adwi, Zinab M Al-Haswsa, Karmen M Alhmmadi, Yasmin A Eissa, Aya Hamdan, Hiba Bawadi, Reema F Tayyem
Nutrition and Health.2023; 29(2): 215. CrossRef - Dietary salt intake predicts future development of metabolic syndrome in the general population
Hiroyuki Takase, Kazusa Hayashi, Fumihiko Kin, Suguru Nakano, Masashi Machii, Shin Takayama, Tomonori Sugiura, Yasuaki Dohi
Hypertension Research.2023; 46(1): 236. CrossRef - High Sodium Intake, as Assessed by Urinary Sodium Excretion, Is Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease or Sarcopenia
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Seung-Soon Im, Hye Soon Kim, Taeg Kyu Kwon, Byoung Kuk Jang
Gut and Liver.2023; 17(3): 456. CrossRef - Trends of Dietary Intakes and Metabolic Diseases in Japanese Adults: Assessment of National Health Promotion Policy and National Health and Nutrition Survey 1995–2019
Muhammad Fauzi, Indri Kartiko-Sari, Hemant Poudyal
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(9): 2350. CrossRef - Determinants of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among Adults in Dill-Chora Referral Hospital, Dire Dawa, East Ethiopia
Tewodros Getnet Amera, Yibekal Manaye Tefera, Tameru Menberu, Aminu Mohammed Yassin
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 3565. CrossRef - Dietary sodium and cardiovascular morbidity/mortality: a brief commentary on the ‘J-shape hypothesis’
Christiana Tsirimiagkou, Kalliopi Karatzi, Antonios Argyris, Eirini D. Basdeki, Panagiota Kaloudi, Mary Yannakoulia, Athanase D. Protogerou
Journal of Hypertension.2021; 39(12): 2335. CrossRef - Associations of Dietary Salt and Its Sources with Hemoglobin A1c in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Not Taking Anti-Diabetic Medications: Analysis Based on 6-Month Intervention with a Moderate Low-Carbohydrate Diet
Hajime Haimoto, Takashi Murase, Shiho Watanabe, Keiko Maeda, Kenji Wakai
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 4569. CrossRef - Association of rheumatoid arthritis and high sodium intake with major adverse cardiovascular events: a cross-sectional study from the seventh Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jeong-Hyeon Bae, Min-Young Shin, Eun Ha Kang, Yun Jong Lee, You-Jung Ha
BMJ Open.2021; 11(12): e056255. CrossRef - Nineteen-year trends in fermented food consumption and sodium intake from fermented foods for Korean adults from 1998 to 2016
Sang Young Kim, Jeanne H Freeland-Graves, Hyun Ja Kim
Public Health Nutrition.2020; 23(3): 515. CrossRef - Dietary Sodium Intake and Health Indicators: A Systematic Review of Published Literature between January 2015 and December 2019
Katherine J Overwyk, Zerleen S Quader, Joyce Maalouf, Marlana Bates, Jacqui Webster, Mary G George, Robert K Merritt, Mary E Cogswell
Advances in Nutrition.2020; 11(5): 1174. CrossRef - Lower Leg Fat Depots Are Associated with Albuminuria Independently of Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Metabolic Syndrome (Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 2008 to 2011)
Eugene Han, Nan Hee Cho, Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 461. CrossRef - Factors Predicting Sodium Intake of Korean Americans with Type 2 Diabetes
Jisook Ko, Kim B. Kim, Gayle M. Timmerman, Angela P. Clark, Miyong Kim
Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health.2018; 20(3): 641. CrossRef - Evaluation of the association between the number of natural teeth and anemia among Korean adults using nationally representative data
Kyungdo Han, Jun‐Beom Park
Journal of Periodontology.2018; 89(10): 1184. CrossRef - Clinical implications of age and sex in the prevalence of periodontitis in Korean adults with diabetes
Kyungdo Han, Jun‑Beom Park
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between underweight and tooth loss among Korean adults
In-Seok Song, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Jun Ryu, Jun-Beom Park
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The Science of Salt: A regularly updated systematic review of the implementation of salt reduction interventions (March–August 2016)
Joseph Alvin Santos, Kathy Trieu, Thout Sudhir Raj, JoAnne Arcand, Claire Johnson, Jacqui Webster, Rachael McLean
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2017; 19(4): 439. CrossRef - Salt-sensitive genes and their relation to obesity
Yong-Pil Cheon, Myoungsook Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(3): 217. CrossRef
- Salt Intake in Adults with Diabetes and Hypertension: The Longitudinal Study of Adult Health-Brasil Study
- Pathophysiology
- Morphologic Changes in Autonomic Nerves in Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy
- Heung Yong Jin, Hong Sun Baek, Tae Sun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(6):461-467. Published online December 11, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.6.461
- 3,533 View
- 40 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Diabetic neuropathy is one of the major complications of diabetes, and it increases morbidity and mortality in patients with both type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Because the autonomic nervous system, for example, parasympathetic axons, has a diffuse and wide distribution, we do not know the morphological changes that occur in autonomic neural control and their exact mechanisms in diabetic patients with diabetic autonomic neuropathy (DAN). Although the prevalence of sympathetic and parasympathetic neuropathy is similar in T1DM versus T2DM patients, sympathetic nerve function correlates with parasympathetic neuropathy only in T1DM patients. The explanation for these discrepancies might be that parasympathetic nerve function was more severely affected among T2DM patients. As parasympathetic nerve damage seems to be more advanced than sympathetic nerve damage, it might be that parasympathetic neuropathy precedes sympathetic neuropathy in T2DM, which was Ewing's concept. This could be explained by the intrinsic morphologic difference. Therefore, the morphological changes in the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves of involved organs in T1DM and T2DM patients who have DAN should be evaluated. In this review, evaluation methods for morphological changes in the epidermal nerves of skin, and the intrinsic nerves of the stomach will be discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impaired Cardiovagal Activity as a Link Between Hyperglycemia and Arterial Stiffness in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Among an Eastern Indian Population: A Cross-sectional Study
Nibedita Priyadarsini, Devineni Likhitha, Madumathy Ramachandran, Kishore Kumar Behera
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetic visceral neuropathy of gastroparesis: Gastric mucosal innervation and clinical significance
Ping‐Huei Tseng, Chi‐Chao Chao, Ya‐Yin Cheng, Chieh‐Chang Chen, Ping‐Hao Yang, Wei‐Kang Yang, Shao‐Wei Wu, Yen‐Wen Wu, Mei‐Fang Cheng, Wei‐Shiung Yang, Ming‐Shiang Wu, Sung‐Tsang Hsieh
European Journal of Neurology.2022; 29(7): 2097. CrossRef - Pathogenesis of Distal Symmetrical Polyneuropathy in Diabetes
Sasha Smith, Pasha Normahani, Tristan Lane, David Hohenschurz-Schmidt, Nick Oliver, Alun Huw Davies
Life.2022; 12(7): 1074. CrossRef - Diabetic Cardiomyopathy and Ischemic Heart Disease: Prevention and Therapy by Exercise and Conditioning
Antonio Crisafulli, Pasquale Pagliaro, Silvana Roberto, Lucia Cugusi, Giuseppe Mercuro, Antigone Lazou, Christophe Beauloye, Luc Bertrand, Derek J. Hausenloy, Manuela Aragno, Claudia Penna
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(8): 2896. CrossRef - Distribution characteristics of sweat gland nerve fibres in normal humans identified by acetylcholinesterase histochemical staining
Li Ling, Yongdan Liu, Yifei Sun, Yun Cai, Ye Jiang, Longjian Chen, Long He, Jinwei Xue
Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery.2020; 189: 105620. CrossRef - Diabetes abolish cardioprotective effects of remote ischemic conditioning: evidences and possible mechanisms
Sakshi Tyagi, Nirmal Singh, Jasleen kaur Virdi, Amteshwar Singh Jaggi
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry.2019; 75(1): 19. CrossRef - Regulation of glucose metabolism by bioactive phytochemicals for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Chao Zhao, Chengfeng Yang, Sydney Tang Chi Wai, Yanbo Zhang, Maria P. Portillo, Paolo Paoli, Yijing Wu, Wai San Cheang, Bin Liu, Christian Carpéné, Jianbo Xiao, Hui Cao
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2019; 59(6): 830. CrossRef - Pulse pressure amplification and cardiac autonomic dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ioanna Eleftheriadou, George C. Drosos, Anastasios Tentolouris, Giorgios Konstantonis, Petros P. Sfikakis, Athanasios D. Protogerou, Nikolaos Tentolouris
Journal of Human Hypertension.2018; 32(8-9): 531. CrossRef - Exposure to hypoglycemia and risk of stroke
Logan Smith, Diya Chakraborty, Pallab Bhattacharya, Deepaneeta Sarmah, Sebastian Koch, Kunjan R. Dave
Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences.2018; 1431(1): 25. CrossRef - Association between the risk of falls and osteoporotic fractures in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Maki Yokomoto-Umakoshi, Ippei Kanazawa, Shiori Kondo, Toshitsugu Sugimoto
Endocrine Journal.2017; 64(7): 727. CrossRef - Diabetes‐induced mechanophysiological changes in the esophagus
Jingbo Zhao, Hans Gregersen
Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences.2016; 1380(1): 139. CrossRef
- Impaired Cardiovagal Activity as a Link Between Hyperglycemia and Arterial Stiffness in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Among an Eastern Indian Population: A Cross-sectional Study
- The Relationship between Anemia and the Initiation of Dialysis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy
- Sun Hee Kim, Kyung Ae Lee, Heung Yong Jin, Hong Sun Baek, Tae Sun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(3):240-246. Published online April 22, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.3.240
- 3,676 View
- 32 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Anemia is associated with various poor clinical outcomes in chronic kidney disease patients. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between anemia and the initiation degree and time of dialysis in type 2 diabetic nephropathy patients.
Methods This observational retrospective study included 130 type 2 diabetic nephropathy patients in Korea. The existence of anemia, the degree and time of dialysis initiation were reviewed. Clinical characteristics and variables were also compared.
Results The levels of hemoglobin and serum creatinine were significantly correlated with the dialysis initiation (
P <0.05) during the 10-year follow-up period. Patients with anemia showed rapid decline of renal function, causing significantly more dialysis initiation (54.1% vs. 5.4%,P <0.05) compare to the patients without anemia. Average time to initiate dialysis in patients with anemia was 45.1 months (range, 8.0 to 115.8 months), which was significantly faster than that (68.3 months [range, 23.3 to 108.8 months]) in patients without anemia (P <0.01). The risk to dialysis initiation was significantly increased in patients with anemia compared to the patients without anemia (adjusted hazard ratio, 8.1; 95% confidence interval, 2.4 to 27.0;P <0.05).Conclusion Anemia is associated with rapid decline of renal dysfunction and faster initiation of dialysis in diabetic nephropathy patients. Therefore, clinicians should pay an earlier attention to anemia during the management of diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microalbuminuria as the Tip of Iceberg in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Associated Diabetic Complications
Sohaib Asghar, Shoaib Asghar, Tayyab Mahmood, Syed Muhammad Hassan Bukhari, Muhammad Habib Mumtaz, Ali Rasheed
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association between Serum Hemoglobin and Renal Prognosis of IgA Nephropathy
Tae Ryom Oh, Su Hyun Song, Hong Sang Choi, Chang Seong Kim, Seung Hyeok Han, Kyung Pyo Kang, Young Joo Kwon, Soo Wan Kim, Seong Kwon Ma, Eun Hui Bae
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(2): 363. CrossRef - Prevalence of anemia in diabetic adult outpatients in Northeast Ethiopia
Temesgen Fiseha, Aderaw Adamu, Melkam Tesfaye, Angesom Gebreweld, Jennifer A. Hirst
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(9): e0222111. CrossRef - Targeted Clinical Metabolite Profiling Platform for the Stratification of Diabetic Patients
Ahonen, Jäntti, Suvitaival, Theilade, Risz, Kostiainen, Rossing, Orešič, Hyötyläinen
Metabolites.2019; 9(9): 184. CrossRef - Effect of high density lipoprotein cholesterol on the relationship of serum iron and hemoglobin with kidney function in diabetes
Ashley N. Williams, Baqiyyah N. Conway
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2017; 31(6): 958. CrossRef
- Microalbuminuria as the Tip of Iceberg in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Associated Diabetic Complications
- Relationship between the Korean Version Survey of the Autonomic Symptoms Score and Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy Parameters in Patients with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
- Sun Hee Kim, Kyung Ae Lee, Heung Yong Jin, Hong Sun Baek, Tae Sun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(5):349-355. Published online October 17, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.5.349
- 5,177 View
- 51 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The Survey of Autonomic Symptom (SAS) scale was reported as an easy instrument to assess the autonomic symptoms in patients with early diabetic neuropathy. In this study, we investigated the relationship between the SAS scale and the parameters of cardiac autonomic neuropathy (CAN) in Korean patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN).
Methods The SAS scale was tested in 30 healthy controls and 73 patients with DPN at Chonbuk National University Hospital, in Korea. The SAS score was compared to the parameters of the CAN test and the total symptom score (TSS) for DPN in patients with DPN.
Results The SAS symptom score and total impact score were increased in patients with DPN compared to the control group (
P =0.01), particularly in sudomotor dysfunction (P =0.01), and vasomotor dysfunction (P =0.01). The SAS score was increased in patients with CAN compared to patients without CAN (P <0.05). Among the diverse CAN parameters, the valsalva ratio and postural hypotension were associated with the SAS score (P <0.05). However, there was no association between the SAS scale and TSS for DPN, and TSS for DPN did not differ between patients with and without CAN.Conclusion SAS is a simple instrument that can be used to assess autonomic symptoms in patients with diabetes and can be used as a screening tool for autonomic neuropathy, particularly for CAN.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Autonomic neuropathic symptoms in patients with diabetes: practical tools for screening in daily routine
Ana Raquel Souza de Azevedo Vieira, Lara Benigno Porto-Dantas, Flaviene Alves do Prado Romani, Patrícia Souza Carvalho, Rodica Pop-Busui, Hermelinda Cordeiro Pedrosa
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Symptomatic diabetic autonomic neuropathy in type 1 diabetes (T1D): Findings from the T1D exchange
Kara Mizokami-Stout, Ryan Bailey, Lynn Ang, Grazia Aleppo, Carol J. Levy, Michael R. Rickels, Viral N. Shah, Sarit Polsky, Bryce Nelson, Anders L. Carlson, Francesco Vendrame, Rodica Pop-Busui
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2022; 36(5): 108148. CrossRef - Clinical Assessment Scales in Autonomic Nervous System Disorders
Eun Bin Cho, Ki-Jong Park
Journal of the Korean Neurological Association.2021; 39(2 Suppl): 60. CrossRef - Peripheral Nerve Conduction And Sympathetic Skin Response Are Reliable Methods to Detect Diabetic Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy
Xiaopu Lin, Chuna Chen, Yingshan Liu, Yu Peng, Zhenguo Chen, Haishan Huang, Lingling Xu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive model to identify the risk of losing protective sensibility of the foot in patients with diabetes mellitus
Esther Chicharro‐Luna, Francisco José Pomares‐Gómez, Ana Belen Ortega‐Ávila, Ana Marchena‐Rodríguez, José Francisco Javier Blanquer‐Gregori, Emmanuel Navarro‐Flores
International Wound Journal.2020; 17(1): 220. CrossRef - The hemodynamic and pain impact of peripheral nerve block versus spinal anesthesia in diabetic patients undergoing diabetic foot surgery
Hou Yee Lai, Li Lian Foo, Siu Min Lim, Chen Fei Yong, Pui San Loh, Sook Hui Chaw, Mohd Shahnaz Hasan, Chew Yin Wang
Clinical Autonomic Research.2020; 30(1): 53. CrossRef - Update on the Impact, Diagnosis and Management of Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes: What Is Defined, What Is New, and What Is Unmet
Vincenza Spallone
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(1): 3. CrossRef - Validation of the Composite Autonomic Symptom Score 31 (COMPASS 31) for the assessment of symptoms of autonomic neuropathy in people with diabetes
C. Greco, F. Di Gennaro, C. D'Amato, R. Morganti, D. Corradini, A. Sun, S. Longo, D. Lauro, G. Pierangeli, P. Cortelli, V. Spallone
Diabetic Medicine.2017; 34(6): 834. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Autonomic Dysfunction Predicts Diabetic Foot Ulcers in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Without Diabetic Polyneuropathy
Jae-Seung Yun, Seon-Ah Cha, Tae-Seok Lim, Eun-Young Lee, Ki-Ho Song, Yu-Bae Ahn, Ki-Dong Yoo, Joon-Sung Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko
Medicine.2016; 95(12): e3128. CrossRef - Retinal Neurodegeneration Associated With Peripheral Nerve Conduction and Autonomic Nerve Function in Diabetic Patients
Kiyoung Kim, Seung-Young Yu, Hyung Woo Kwak, Eung Suk Kim
American Journal of Ophthalmology.2016; 170: 15. CrossRef - Screening of Autonomic Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Bo Kyung Koo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(5): 346. CrossRef
- Autonomic neuropathic symptoms in patients with diabetes: practical tools for screening in daily routine

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





